Graphs II: Directed Graphs & Advanced Algorithms
This module explores directed graphs, weighted graphs, and advanced graph algorithms including Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm and topological sorting.
Learning Objectives
Core Concepts
- Understand directed and weighted graphs
- Implement Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm
- Learn topological sorting and its applications
- Understand cycle detection in directed graphs
Skills Development
- Graph algorithm optimization techniques
- Path-finding strategies
- Graph representation for directed networks
- Real-world problem-solving with graph algorithms
Prerequisites
Required Knowledge
- Basic graph theory concepts
- BFS and DFS traversal techniques
- Priority queues and heaps
- Graphs I module content
Recommended Preparation
- Review adjacency list and matrix representations
- Practice with queue and priority queue implementations
- Refresh knowledge of time and space complexity
- Explore network flow problems
Video Lectures
Directed Graphs & Representations
Key Concepts Covered:
- Directed graph properties
- Representing directed edges
- In-degree and out-degree
- Applications of directed graphs
Dijkstra's Shortest Path Algorithm
Key Concepts Covered:
- Weighted graph fundamentals
- Step-by-step Dijkstra's algorithm
- Priority queue optimization
- Time and space complexity analysis
Topological Sorting
Key Concepts Covered:
- Directed acyclic graphs (DAGs)
- Topological sort algorithms
- DFS-based implementation
- Applications in scheduling and dependency resolution
Dijkstra's Algorithm Implementation
Java Implementation
import java.util.*;
public class DijkstraAlgorithm {
static class Edge {
int destination;
int weight;
Edge(int destination, int weight) {
this.destination = destination;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
static class Graph {
private int V; // Number of vertices
private List> adjList;
public Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
adjList = new ArrayList<>(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public void addEdge(int source, int destination, int weight) {
adjList.get(source).add(new Edge(destination, weight));
}
public int[] dijkstra(int source) {
// Create a min heap to store vertices and their distances
PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
// Initialize distances array
int[] distance = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(distance, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
distance[source] = 0;
// Add source to min heap
minHeap.add(new int[]{source, 0});
while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
int[] current = minHeap.poll();
int u = current[0]; // Current vertex
int dist = current[1]; // Distance from source to u
// If current distance is greater than the calculated one, skip
if (dist > distance[u]) continue;
// Check all neighbors of u
for (Edge edge : adjList.get(u)) {
int v = edge.destination;
int weight = edge.weight;
// If there is a shorter path to v through u
if (distance[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE &&
distance[u] + weight < distance[v]) {
// Update distance of v
distance[v] = distance[u] + weight;
minHeap.add(new int[]{v, distance[v]});
}
}
}
return distance;
}
}
// Driver code to test the implementation
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 5;
Graph graph = new Graph(V);
// Add edges (source, destination, weight)
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 4);
graph.addEdge(0, 2, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 3, 1);
graph.addEdge(2, 1, 2);
graph.addEdge(2, 3, 5);
graph.addEdge(3, 4, 3);
// Calculate shortest paths from source 0
int[] distances = graph.dijkstra(0);
// Print the result
System.out.println("Shortest distances from source 0:");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
System.out.println("To vertex " + i + ": " + distances[i]);
}
}
} 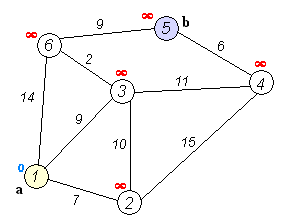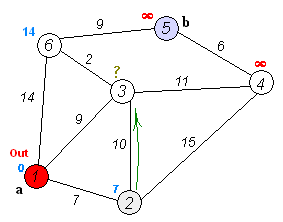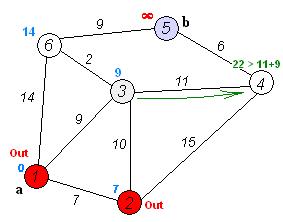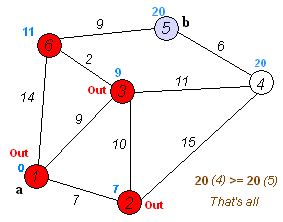
Visual representation of Dijkstra's algorithm finding the shortest path
Topological Sort Implementation
Java Implementation
import java.util.*;
public class TopologicalSort {
static class Graph {
private int V; // Number of vertices
private List> adjList;
public Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
adjList = new ArrayList<>(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public void addEdge(int source, int destination) {
adjList.get(source).add(destination);
}
// Topological Sort using DFS
public List topologicalSort() {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// Call recursive helper function for all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack);
}
}
// Create result list from stack
List result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result.add(stack.pop());
}
return result;
}
private void topologicalSortUtil(int v, boolean[] visited, Stack stack) {
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all adjacent vertices
for (Integer neighbor : adjList.get(v)) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
topologicalSortUtil(neighbor, visited, stack);
}
}
// Push current vertex to stack after all neighbors are visited
stack.push(v);
}
}
// Driver code to test the implementation
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 6;
Graph graph = new Graph(V);
// Add edges for a DAG representing course prerequisites
graph.addEdge(5, 2);
graph.addEdge(5, 0);
graph.addEdge(4, 0);
graph.addEdge(4, 1);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.addEdge(3, 1);
// Perform topological sort
List result = graph.topologicalSort();
// Print the result
System.out.println("Topological Sort Order:");
for (Integer vertex : result) {
System.out.print(vertex + " ");
}
}
} 
Example of a directed acyclic graph (DAG) suitable for topological sorting
Guided Practice
For additional hands-on practice and in-depth exercises on directed graphs and graph algorithms, check out our comprehensive guided project:
Practice Exercises
Directed Graph Exercises
Practice these directed graph problems:
- Course Schedule - LeetCode 207
- Course Schedule II - LeetCode 210
- Find Eventual Safe States - LeetCode 802
- Keys and Rooms - LeetCode 841
Shortest Path Exercises
Practice these shortest path problems:
- Network Delay Time - LeetCode 743
- Cheapest Flights Within K Stops - LeetCode 787
- Path With Minimum Effort - LeetCode 1631
- Path With Maximum Probability - LeetCode 1514
Topological Sort Exercises
Practice these topological sorting problems:
- Alien Dictionary - LeetCode 269
- Sequence Reconstruction - LeetCode 444
- Minimum Height Trees - LeetCode 310
- Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies - LeetCode 1203
Advanced Graph Exercises
Challenge yourself with these advanced graph problems:
- Critical Connections in a Network - LeetCode 1192
- Reconstruct Itinerary - LeetCode 332
- Evaluate Division - LeetCode 399
- Parallel Courses - LeetCode 1136